A technical indicator which is used to know current situation of prices whether prices are low, high or stable is called Bollinger Bands BB. It is a very popular indicator and which was developed by John Bollinger.
John Bollinger was a trader, analyst, and teacher who created Bollinger Bands (BB) in the early 1980s.
The indicator meets the need to observe changes in volatility.
Bollinger Bands are generally used by the traders to determine overbought and oversold zones, to confirm divergences between prices and indicators, and to project price targets.
Bollinger Bands consist of three-line bands that are made in relation to prices.
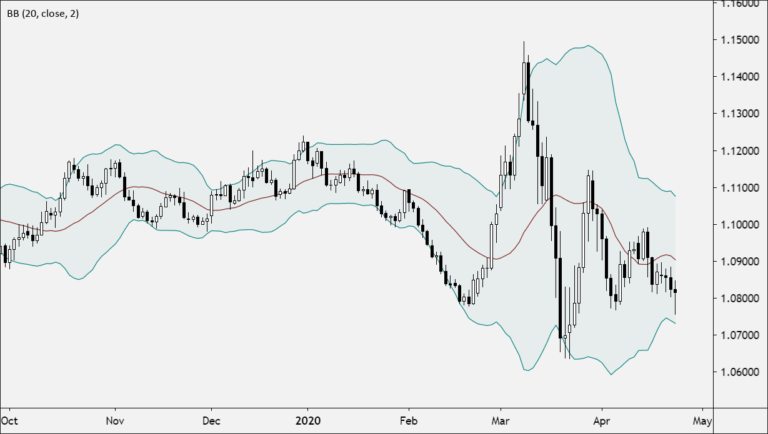
The three lines:
Upper Band
Middle Line
Lower Band
The line in the middle is usually a Simple Moving Average (SMA) for the 20 days duration.
The SMA then acts as a base for the Upper and Lower Bands.
The upper and lower bands are used as a way to measure volatility by looking at the relationship between the bands and the price.
Typically the Upper and Lower Bands are set to two standard deviations away from the SMA (The Middle Line), but can usually be adjusted by the trader.
The bands becomes wider on the increase of volatility. Likewise, as volatility decreases, the gap between bands narrows.
Parameters
Period (20) –The number, or duration, of the bar is used to calculate the study. John Bollinger recommends the best period of 20 or 21 periods and warns that less than ten periods do not work well.
Band Width (2) – The half-width of the band in terms multiples of standard deviation. Typically, “2” is used.
Calculation
First, calculate a simple moving average. Next, calculate the standard deviation (SD) over the same number of periods as the simple moving average (SMA).
For the upper band, add the standard deviation(SD) to the simple moving average (SMA). For the lower band, subtract the standard deviation (SD) from the simple moving average. (SMA)
Typical values used:
Short term: 10-period moving average, bands at 1.5 standard deviations. (1.5 times the standard dev. +/- the SMA)
Medium-term: 20-period moving average, bands at 2 standard deviations.
Long term: 50-period moving average, bands at 2.5 standard deviations.
How Bollinger Bands Work
When the bands tighten during a period of low volatility, it raises the likelihood of a sharp price move in either direction. This may begin a trending move. Watch out for a false move in the opposite direction which reverses before the proper trend begins.
When the bands separate by an unusually large amount, volatility increases and any existing trend may be ending.
Prices have a tendency to bounce within the bands’ envelope, touching one band then moving to the other band. You can use these swings to help identify potential profit targets. For example, if a price bounces off the lower band and then crosses above the moving average, the upper band then becomes the profit target.
Price can exceed or hug a band envelope for prolonged periods during strong trends. On divergence with a momentum oscillator, you may want to do additional research to determine if taking additional profits is appropriate for you.
A strong trend continuation can be expected when the price moves out of the bands. However, if prices move immediately back inside the band, then the suggested strength is negated.
How to Use Bollinger Bands
Traders generally use Bollinger Bands to determine overbought and oversold zones, to confirm divergences between prices and studies, and to project price targets.
The wider the bands, the greater the volatility. The narrower the bands, the lesser the volatility.
Some traders use Bollinger Bands with other technical indicators, such as RSI.
If price touches the Upper Band and the other technical indicator does not confirm the upward move (i.e. there is divergence), a sell signal is generated.
If the other technical indicator confirms the upward move, no sell signal is generated, and in fact, a buy signal may be indicated.
If price touches the Lower Band and the other technical indicator does not confirm the downward move, a buy signal is generated.
If the other technical indicator confirms the downward move, no buy signal is generated, and in fact, a sell signal may be indicated.
Another strategy is to the Bollinger Bands by itself.
In this approach, a chart top occurring above the Upper Band followed by a top below the upper band generates a sell signal.
On the other hand, a chart bottom occurring below the Lower Band followed by a bottom above the lower band generates a buy signal.
Bollinger Bands also helps determine overbought and oversold markets.
When prices move closer to the upper band, the currency pair is becoming overbought, and as the prices move closer to the lower band, the currency pair is becoming oversold.
The price momentum should also be taken into account. When a price enters an overbought or oversold area, it may become even more so before it reverses.
You should always look for evidence of price weakening or strengthening before anticipating a trend reversal.
Bollinger Bands differ from similar indicators such as Keltner Channels or Moving Average Envelopes in such a way that the width of the range is not constant, but it changes according to historical volatility.
If volatility increases, the band becomes wider, and if volatility decreases, the band becomes narrower.
A significant widening of the band may signal the end of a trend.
A significant narrowing of the band implies the start of a new trend.
Summary
Bollinger Bands consist of upper and lower bands based, middle band (SMA) based on standard deviation (SD) that shrink and widen with volatility.
Bands are a useful tool for analyzing and monitoring the strength of a trend when a reversal may occur.
Bollinger Bands are not predictive though. They are always based on historical information and therefore react to price changes, but don’t anticipate price changes.
Like other indicators, Bollinger Bands are used in conjunction with other indicators, price analysis, and risk management as part of the overall trading plan.
A
Abandoned Baby | Account Statement Report | Account Value | Accumulation Area | Accumulative Swing Index ASI | Address | ADDY | ADP National Employment Report | Advance Or Decline Index | Afghanistan Afghanis | Agency Model | Aggressor | Alan Bollard | Alan Greenspan | Albania Leke | Algerian Algeria Dinars | Alligator | Altcoin | Analysts | Andrews Pitchfork | Angela Merkel | Angola Kwanza | Anti Money Laundering AML | ANZ Commodity Price Index | Application Programming Interface API | Appreciation | Arbitrage | Argentina Pesos | Armenian Drams | Aroon Oscillator | Aroon Up And Down | Aruban Guilder | Ascending Channel | Ascending Trend Line | Ascending Triangle | ASIC Mining | Asset | Asset Purchase Programme APP | Asset Purchases | Asymmetric Encryption | Asymmetric Slippage
B
Bag | Bag Holder | Bahmas Dollars | Bahrain Dinars | Bail In | Bail Out | Balance Of Trade | Baltic Dry Index | Bangladesh Taka | Bank Levy | Bank Of Canada BOC | Bank Of England BOE | Bank Of International Settlement BIS | Bank Of Japan BoJ | Bank Run | Bank Run | Banking Institutions | Bar Chart | Barbados Dollars | Base Currency | Base Rate | Basing | Basing Point | Bear | Bear Flag | Bear Market | Bear Trap | Bearish | Binary Options | Bitcoin Cash | Bitcoin Maximalist | Bitcoin Or BTC | Block | Block Explorer | Block Header | Block Height | Block Reward | Blockchain | Blue Chip | Bolivia Bolivianos | Bollinger Bands | Bond | Bond Auction | Bond Yeild | Book | Boris Schlossberg | Botswana Pulas | Brazilian Brazil Real | Breakdown | Breakeven | Breakout | Brent Crude | Bretton Woods Agreement Of 1944 | BRIC | Broadening Formation | Broker | BTD | BTFD | Bucket Shop | Bulgarian Leva | Bull | Bull Flag | Bull Market | Bull Trap | Bullish | Bullish Engulfing Pattern | Bundesbank | Burundi Francs | Business Inventories | Buy Side | Buying Pressure
C
Cable | Camarilla Pivot Points | Cambist | Cambodian Riels | Canadian Dollar | Cape Verde Escudos | Carbon Credits | Cardano ADA | Carry Trade | Cash Market | Catalyst | Cayman Islands Dollars | Cboe Eurocurrency Volatility Index | Central Bank | Central Bank Digital Currency | Central Bank Intervention | Central Counterparty Clearing Houses CCPs | Central Limit Order Book Or CLOB | Chaikin Oscillator | Chart Pattern | Chartist | Chicago PMI | Chilean Peso | Chinese Renminbi | Chinese Yuan | Christine Lagarde | Circulating Supply | Cleared Funds | Clearing | Clearing Price | Client | Closed Position | Cloud Mining | Coin Age | Cold Storage | Collateral | Colombian Pesos | Comdoll | Commercial Corporations | Commission | Commitments Of Traders Report Or COT | Commodity | Commodity Channel Index Or CCI | Commodity Futures Trading Commission CFTC | Commodity Research Bureau Index | Commodity Trading Advisor CTA | Communaute Financiere Africaine Francs | Comoros Francs | Completeness | Compound COPM | Comptoirs Francais Du Pacifique Francs | Conference Board Consumer Confidence Index CCI | Confirmation | Confluence | Congo Congolese Francs | Consensus Algorithm | Consolidation | Consumer Price Index CPI
ForexTrading.pk